Difference between revisions of "PAM configuration for Windows Active Directory via SSSD"
(Created page with "== Installation == Install the necessary packages, for Debian and derivates the packages are <code>sssd</code>, <code>adcli</code>, <code>realmd</code>, <code>oddjob</code>, <...") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Declarations == | ||
| + | In this documentation, several values will be used for hostnames, domain name, usernames and password. These are only examples and must be changed according to your environment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | AD server: | ||
| + | Hostname and aliases: 192.168.1.65 | ||
| + | name alias: winad | ||
| + | local hostname seen from Windows side: dc.winad.c-works.net | ||
| + | Active directory domain name: winad.c-works.net | ||
| + | Kerberos realm: WINAD.C-WORKS.NET | ||
| + | (The kerberos realm is the domain name in upper case characters!) | ||
| + | |||
| + | User for connecting to domain (with administrative rights, but without permission to login interactively on AD server): | ||
| + | Username: pamauth | ||
| + | Password: Test1234 | ||
| + | User to be authentificated (as an example) and configured in OS4X: | ||
| + | Username: adUsername1 | ||
| + | Password: OS4Xpwd | ||
| + | |||
| + | Username: os4x | ||
| + | Password: Test1234 | ||
| + | |||
| + | All commands on the Linux side are executed in the context of the user "<code>root</code>". | ||
| + | |||
== Installation == | == Installation == | ||
Install the necessary packages, for Debian and derivates the packages are <code>sssd</code>, <code>adcli</code>, <code>realmd</code>, <code>oddjob</code>, <code>oddjob-mkhomedir</code> and <code>packagekit</code> | Install the necessary packages, for Debian and derivates the packages are <code>sssd</code>, <code>adcli</code>, <code>realmd</code>, <code>oddjob</code>, <code>oddjob-mkhomedir</code> and <code>packagekit</code> | ||
apt install sssd adcli realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir packagekit | apt install sssd adcli realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir packagekit | ||
Make sure DNS is pointing to your AD server(s) by checking <code>/etc/resolv.conf</code> and it having it contain an entry with an AD server IP, if it’s missing go ahead and add it, as the first entry. | Make sure DNS is pointing to your AD server(s) by checking <code>/etc/resolv.conf</code> and it having it contain an entry with an AD server IP, if it’s missing go ahead and add it, as the first entry. | ||
| + | |||
=== systemd === | === systemd === | ||
If your network is managed by systemd, you cannot edit <code>/etc/resolv.conf</code> directly. Install resolvconf (if not already installed) | If your network is managed by systemd, you cannot edit <code>/etc/resolv.conf</code> directly. Install resolvconf (if not already installed) | ||
apt install resolvconf | apt install resolvconf | ||
| − | Edit <code>/etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head</code> and add your AD: <code>nameserver 192.168. | + | Edit <code>/etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head</code> and add your AD: <code>nameserver 192.168.1.65</code> and apply the change: |
resolvconf --enable-updates | resolvconf --enable-updates | ||
resolvconf -u | resolvconf -u | ||
| + | |||
== Join AD == | == Join AD == | ||
Now you can issue the <code>realm join</code> command with the domain name in order to join the domain. | Now you can issue the <code>realm join</code> command with the domain name in order to join the domain. | ||
| − | realm join | + | realm join WINAD.C-WORKS.NET |
It will default to use the Administrator user, add the <code>-U</code> flag to specify a different user account to join the domain. | It will default to use the Administrator user, add the <code>-U</code> flag to specify a different user account to join the domain. | ||
| − | realm join -U | + | realm join -U pamauth AD.EXAMPLE.COM |
Now see if it works, and issue an id command. | Now see if it works, and issue an id command. | ||
| − | id | + | id pamauth@WINAD.C-WORKS.NET |
If you want to use short names, edit <code>sssd.conf</code> and set <code>use_fully_qualified_names</code> to <code>false</code>. | If you want to use short names, edit <code>sssd.conf</code> and set <code>use_fully_qualified_names</code> to <code>false</code>. | ||
| + | |||
== Advanced == | == Advanced == | ||
sssd provides alternative directory servers modules, you can find detailed documentation in the [https://sssd.io/docs/introduction.html official docs]. | sssd provides alternative directory servers modules, you can find detailed documentation in the [https://sssd.io/docs/introduction.html official docs]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Configure PAM to use SSSD == | ||
| + | Create or edit the file "<code>/etc/pam.d/os4x</code>" to contain the following line in order to allow OS4X PAM authentification to use SSSD (which now uses Active Directory): | ||
| + | auth required pam_sssd.so | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Configure user to authentificate via PAM == | ||
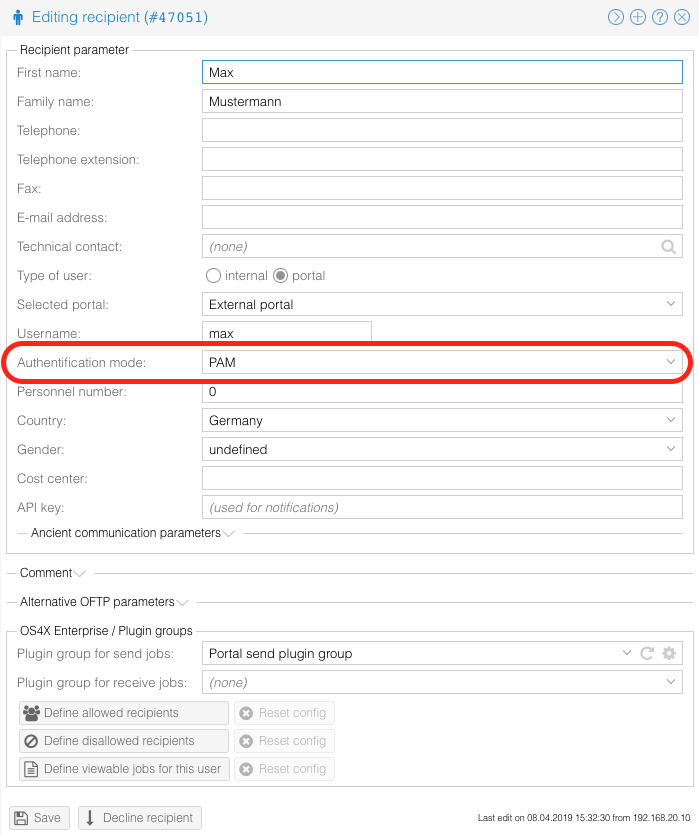
| + | You can now configure your OS4X Webaccess users to use PAM as authentification method: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:OS4Xadmin configure user PAM auth.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can also use the username declaration including the domain name: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:OS4X webaccess login with domain user.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:50, 27 November 2024
Declarations
In this documentation, several values will be used for hostnames, domain name, usernames and password. These are only examples and must be changed according to your environment.
AD server:
Hostname and aliases: 192.168.1.65
name alias: winad
local hostname seen from Windows side: dc.winad.c-works.net
Active directory domain name: winad.c-works.net
Kerberos realm: WINAD.C-WORKS.NET
(The kerberos realm is the domain name in upper case characters!)
User for connecting to domain (with administrative rights, but without permission to login interactively on AD server):
Username: pamauth Password: Test1234
User to be authentificated (as an example) and configured in OS4X:
Username: adUsername1 Password: OS4Xpwd
Username: os4x Password: Test1234
All commands on the Linux side are executed in the context of the user "root".
Installation
Install the necessary packages, for Debian and derivates the packages are sssd, adcli, realmd, oddjob, oddjob-mkhomedir and packagekit
apt install sssd adcli realmd oddjob oddjob-mkhomedir packagekit
Make sure DNS is pointing to your AD server(s) by checking /etc/resolv.conf and it having it contain an entry with an AD server IP, if it’s missing go ahead and add it, as the first entry.
systemd
If your network is managed by systemd, you cannot edit /etc/resolv.conf directly. Install resolvconf (if not already installed)
apt install resolvconf
Edit /etc/resolvconf/resolv.conf.d/head and add your AD: nameserver 192.168.1.65 and apply the change:
resolvconf --enable-updates resolvconf -u
Join AD
Now you can issue the realm join command with the domain name in order to join the domain.
realm join WINAD.C-WORKS.NET
It will default to use the Administrator user, add the -U flag to specify a different user account to join the domain.
realm join -U pamauth AD.EXAMPLE.COM
Now see if it works, and issue an id command.
id pamauth@WINAD.C-WORKS.NET
If you want to use short names, edit sssd.conf and set use_fully_qualified_names to false.
Advanced
sssd provides alternative directory servers modules, you can find detailed documentation in the official docs.
Configure PAM to use SSSD
Create or edit the file "/etc/pam.d/os4x" to contain the following line in order to allow OS4X PAM authentification to use SSSD (which now uses Active Directory):
auth required pam_sssd.so
Configure user to authentificate via PAM
You can now configure your OS4X Webaccess users to use PAM as authentification method:
You can also use the username declaration including the domain name: